Gray Matter Volume Changes Following Reading Intervention in Dyslexic Children
Krafnick, A. J., Flowers, D. L., Napoliello, E. M., & Eden, G. F. (2011). Gray matter volume changes following reading intervention in dyslexic children. Neuroimage, 57, 733-741. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.062
Background
In this study, 11 dyslexic students were pretested on a battery of reading assessments, received eight weeks of Seeing Stars instruction to develop symbol imagery for reading, were retested, and then tested again eight weeks later. Students also received brain scans (magnetic resonance imaging) to measure gray matter volume at the three different points in time. This experiment investigated the constructs of Dual Coding Theory using the Seeing Stars program. Instruction was delivered by teachers who were trained in the programs.
Results
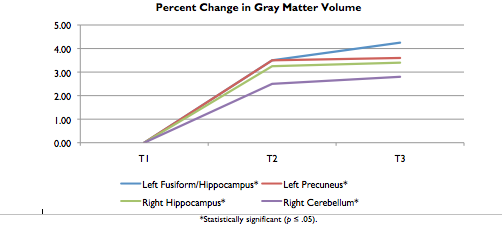
On average, pretest (T1) to retest (T2) results were statistically significant in all brain regions (results from T2 to T3 were not statistically different). Similarly, test scores revealed a statistically significant increase from pretest to retest (results from T2 to T3 were not statistically different). The results of this study support the Dual Coding Theory model of cognition and illustrate that instruction in the Seeing Stars program leads to increased brain structure and improved reading. Follow-up results showed that improvements were maintained.